DevOps Key Principles: A Detailed Overview
In the world of modern software development, speed, reliability and quality are no longer optional they’re essential. Organizations face growing pressure to deliver software faster, adapt to market changes and improve customer experiences. To achieve this, businesses have turned to DevOps, a cultural and technical movement that bridges the gap between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops).
But DevOps isn’t just about adopting tools or automating pipelines. At its heart, it’s a philosophy built on key principles that guide teams to work more efficiently, collaboratively and effectively. Let’s take a deeper look at the core principles of DevOps and how they transform the software delivery lifecycle.
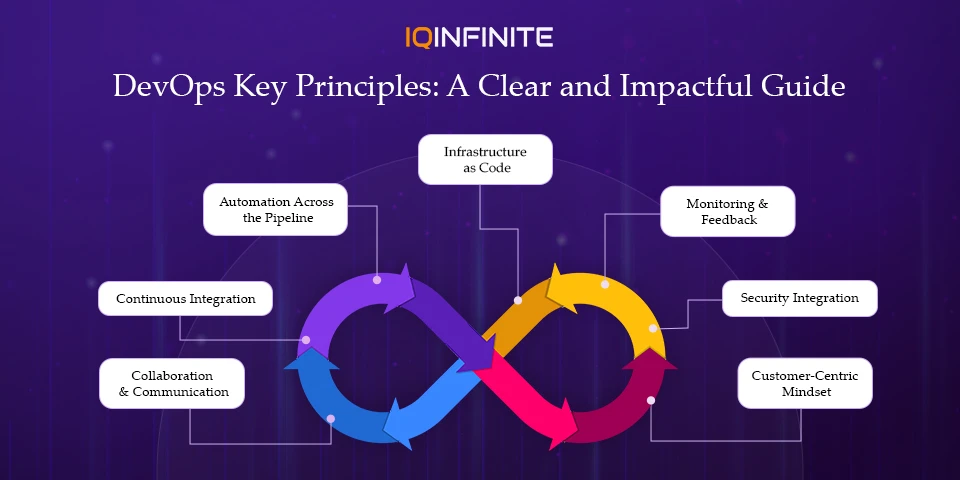
1. Collaboration and Communication
• Development, QA, security and operations work as a single unit.
• Shared responsibility ensures that everyone is accountable for software quality and delivery.
• Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams or Jira enhance communication and transparency.
This principle ensures faster resolution of issues, better alignment with business goals and smoother workflows.
2. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
• Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently merge their code into a shared repository. Automated builds and tests run to detect issues early.
• Continuous Delivery (CD): The validated code is automatically deployed to staging or production environments, reducing release friction.
The benefit? Faster time-to-market, fewer errors in production and a more reliable release process.
3. Automation Across the Pipeline
Examples include:
• Automated Testing - Unit, integration and end-to-end tests triggered with each commit.
• Automated Infrastructure - Tools like Terraform or Ansible to spin up servers or containers.
• Automated Deployments - CI/CD pipelines deploy code seamlessly to different environments.
This allows teams to focus on innovation rather than repetitive manual tasks.
4. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Key advantages:
• Consistency: Environments can be replicated without discrepancies.
• Scalability: Infrastructure can scale up or down easily using scripts.
• Version Control: Infrastructure changes are tracked just like software code.
Popular IaC tools include Terraform, AWS CloudFormation and Ansible. With IaC, deploying complex environments becomes predictable, repeatable and faster.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
• Application Monitoring: Tools like Prometheus, Grafana and Datadog provide insights into application performance.
• Infrastructure Monitoring: Ensures servers, networks and cloud resources are running smoothly.
• User Feedback: Integrating customer insights helps teams improve user experience.
This creates a feedback loop problem are identified quickly and improvements are continuously applied.
6. Security Integration (DevSecOps)
• Automated Security Testing: Vulnerability scans and code analysis during CI/CD.
• Shift-Left Security: Security checks start early in development rather than at the end.
• Compliance as Code: Regulatory requirements are built into pipelines.
This ensures software is secure by design, not patched later.
7. Customer-Centric Mindset
• Shorter release cycles mean customers get new features quickly.
• Monitoring and feedback loops ensure user needs are continuously addressed.
• Collaboration ensures the final product is aligned with business goals and customer expectations.
This customer-first approach is what makes DevOps so impactful for businesses.
Conclusion
In a world where technology evolves rapidly, adopting these DevOps principles isn’t just an advantage it’s a necessity for staying competitive.
